SM Contact Engineering has done significant work to investigate the most common industrial crimp standards in terms of components requirements, dimensions, compression rate and contact resistance. Standards in question are
PSA 9634115099, VW 60330, USCAR-21, TDK-EPCOS F61207-R3308 and Bosch N42AP 730 (2014).
1. Ranges of components
Ranges of components which fall within the norms are limited to multi-stranded cables and crimp barrels. There are only two cases when splice technology is considered: in one of the norms – for single sensor connection to a flexible wire, in the others – with the same requirements as for crimp connection, if not specified by the supplier.
2. Wire materials
As for wire materials flexible copper is the only option. Exotic materials are mentioned as acceptable in the only one norm, if specified by the supplier.
3. Requirements to dimensions
Requirements to dimensions are applicable to wire and terminal connections, but when we talk about special components it is necessary to dispense with a norm to get maximum interconnection surface.
4. Compression rate
There are different norms of measuring the сompacting (compression) rate: by comparing initial components’ surface and overall surface after crimping or measuring terminal compression. Following this instructions it is not possible to achieve recommended minimum ratio, which is 15%, with PCB-wire or hard-soft components connections (e.g. sensor and fiber, core wire wrapped with a cooper spiral, inox pin with a cooper wire). Since PCB can be destroyed and harder materials cannot be compressed so much, it is necessary not to include such a component into compression measurement.
5. Contact resistance
Concerning the contact resistance recommended maximum level is from 0.55 to 1 mOhm that complies with various connections. According the above-mentioned norms resistance is to be measured between two points: point of the wire closest to entering into the crimp and point of the terminal closest to the end of the wire. But when we talk about connection between 2 components (for example, wires) we have to violate norms and move the measuring points to free surface of components, and they might be unique for particular part.
As can be seen from the above nowadays electrical connections are not limited to wire & terminal, which leads to the certain opacity of norms. Exotic materials (aluminum, steel, fiber, etc.) and components (e.g. battery tab, PCB pin, sensor, etc.) are considered in few norms providing that the supplier is in charge of defining reference criteria. Here comes a question: how to specify optimal connection parameters? The answer is IEC norm which gives corresponding test schedules and techniques. Further details about IEC methodology will be provided in the next issue of “Useful tips from Splice Crimping Seminar”.
For reference, PSA is created by the Society of Automotive Engineers for automotive crimp connections; VW 60330 is the only process-oriented specification indicating how often testing should be done; USCAR-21 Crimp Performance Specification defines basic test methods and requirements for solderless crimped connections and contents a series of tests completed in two phases: thermal shock and high-humidity steam aging (the US Council for Automotive Research LLC (USCAR) is the collaborative automotive technology company for Chrysler Group LLC, Ford Motor Company and General Motors); Bosch N42AP 730 (2014) includes general requirements and test methods for cold, electroless processing of crimp contacts with open crimping barrels in conjunction with solid and stranded wires.
[caption id="attachment_2308" align="aligncenter" width="449"]
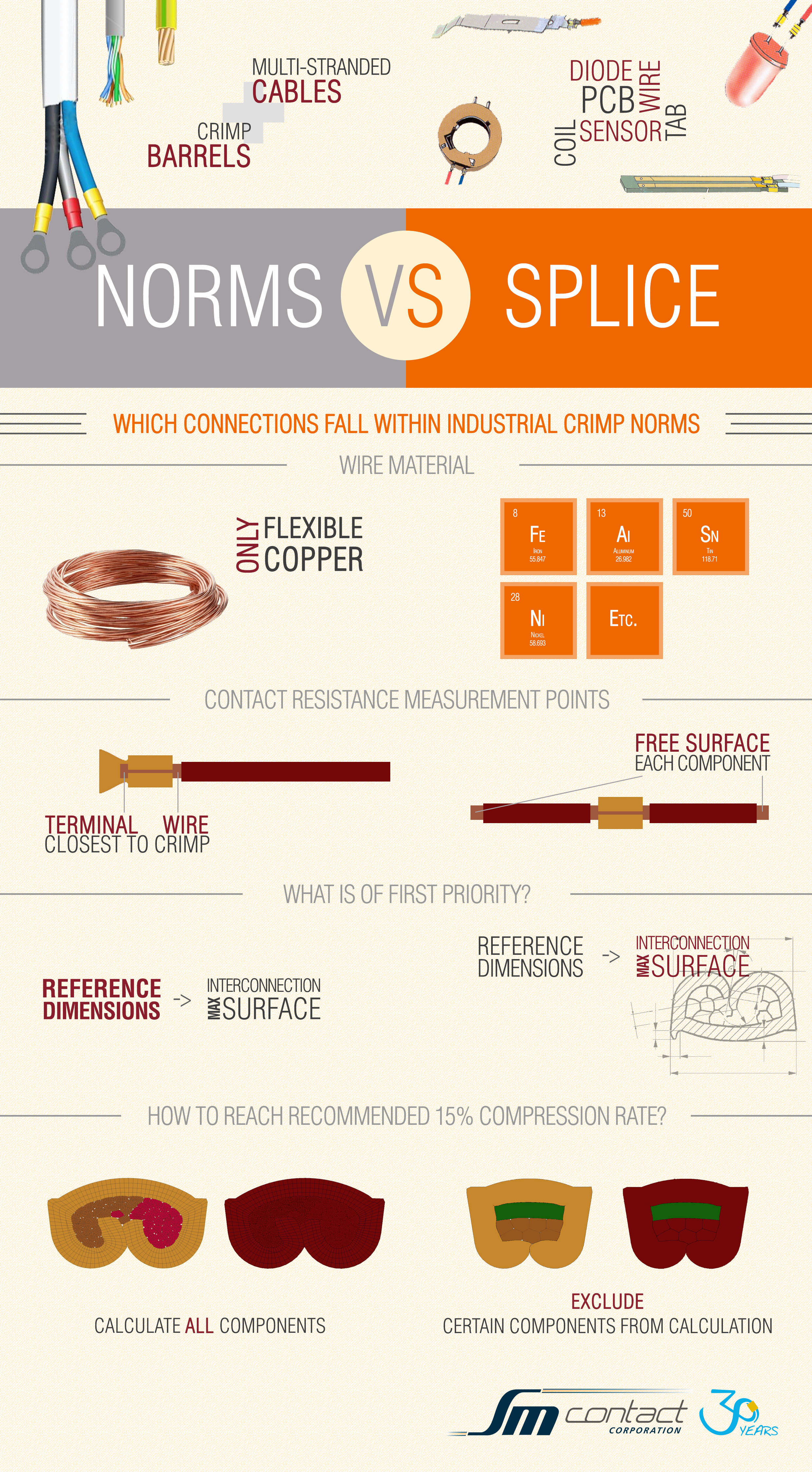
Which connections fall within industrial crimp norms?[/caption]
Previous "Useful tips":
Next "Useful tips":
Сохранить
Сохранить Which connections fall within industrial crimp norms?[/caption]
Previous "Useful tips":
Next "Useful tips":
Which connections fall within industrial crimp norms?[/caption]
Previous "Useful tips":
Next "Useful tips":
 English
English
 Chinese
Chinese










 +86- 20-3992 0957
+86- 20-3992 0957